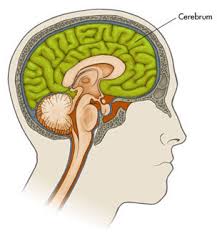
Brain
a. cerebrum
i. hemispheres right and left
ii. frontal lobe - higher intellectual functions,social behavior, personality
iii. parietal lobe - interprets sensory input
iv. temporal lobe - hearing, taste and smell
v. occipital lobe - vision
b. cerebellum - provide equilibrium and muscle coordination
c. brain stem - midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata; controls basic body functions and relays impulses to and from spinal cord
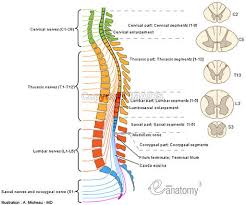
Spinal cord
a. descending tract - anterior portion of cord carrying motor information
b. ascending tract
i. the posterior portion of cord, carrying sensory information
ii. 31 segments
eight cervical: neck and upper extremities
12 thoracic: thoracic and abdomen
five lumbar: lower extremities
five sacral: lower extremities, urine and bowel control
one coccygeal
Peripheral nervous system - carries information to and from the CNS
1. Motor nerves
2. Sensory nerves
C. Autonomic nervous system - regulates body's internal environment
1. Sympathetic - prepares body for fight or flight; used only as needed
2. Parasympathetic - controls normal body functioning for day to day activities, e.g., increases muscle tone, maintains secretions; maintains heart rate within normal limits; maintains peristalsis
Cranial nerves
These nerves are the vital bridges between the brain and the rest of the body.
1 Olfactory
2 Optic
3 Oculomotor
4 Trochlear
5 Trigeminal
6 Abducens
7 Facial
8 Auditory
9 Glossopharyngeal
10 Vagus
11 Spinal
12 Hypoglossal
No comments:
Post a Comment